

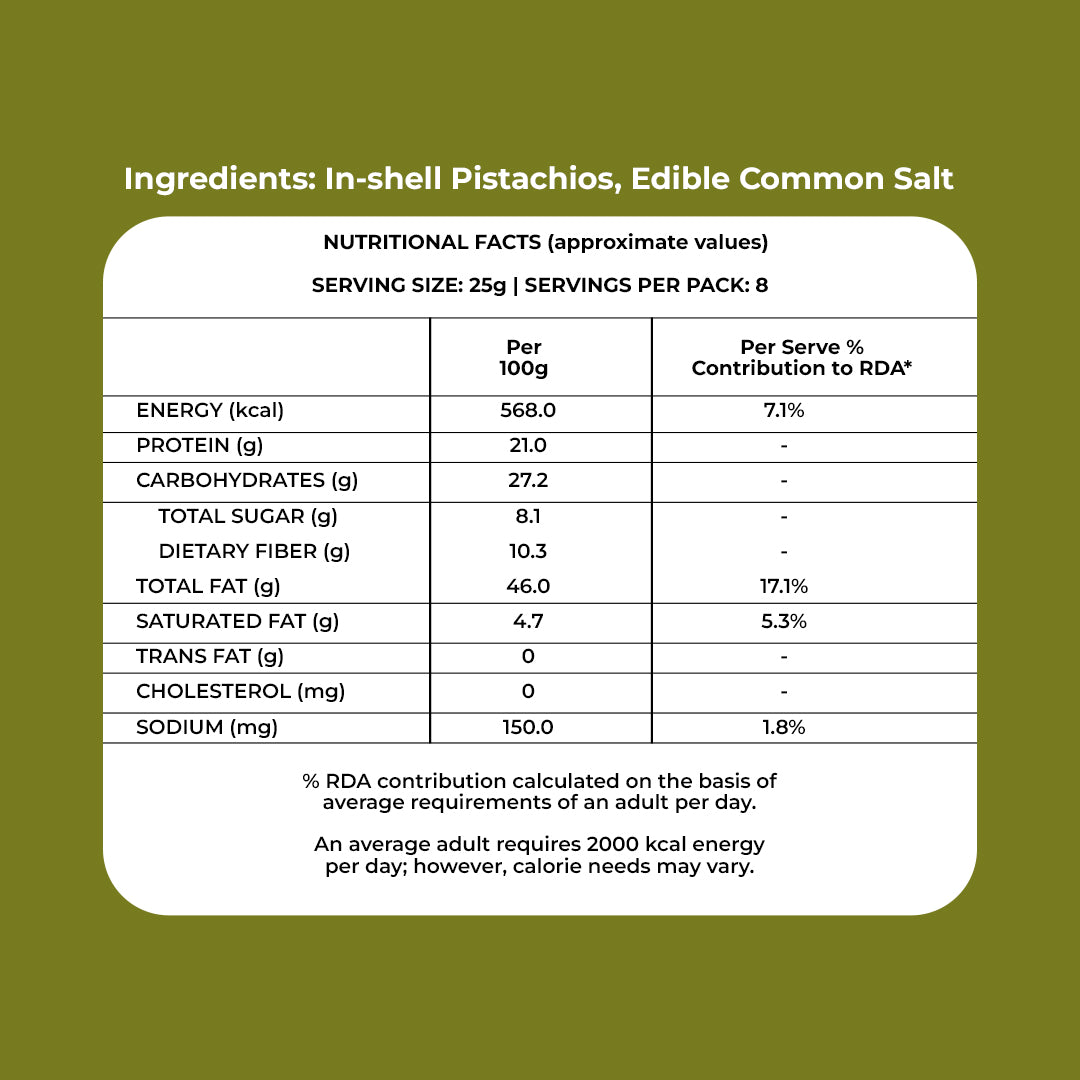




PREMIUM CALIFORNIA PISTACHIO
- Rs. 639.00
Rs. 650.00- Rs. 639.00
- Unit price
- per
MRP (Inclusive of all taxes)

PREMIUM CALIFORNIA PISTACHIO
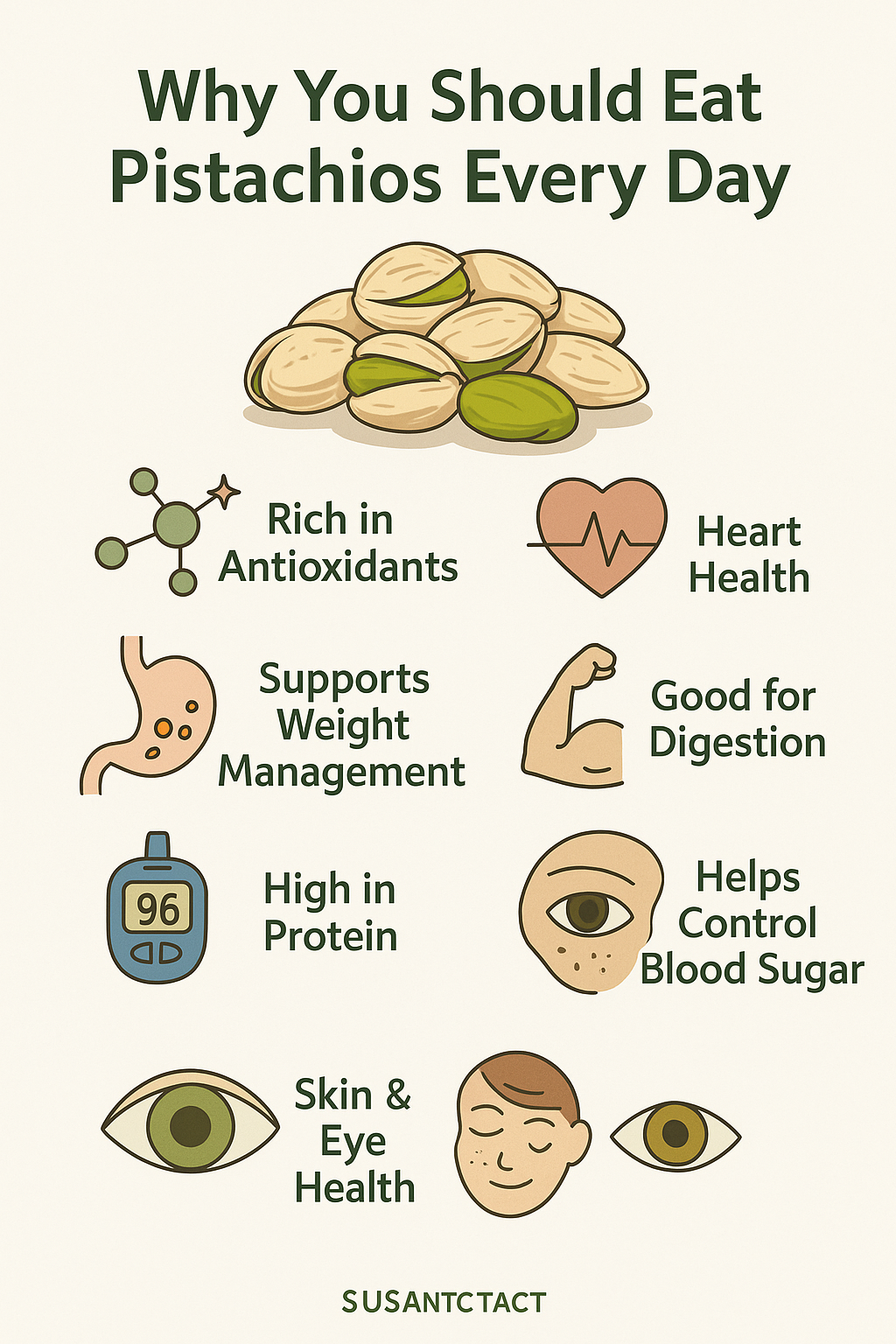
🌿 Why You Should Eat Pistachios Every Day
🧠 1. Rich in Antioxidants
Pistachios are among the most antioxidant-rich nuts. They contain lutein and zeaxanthin — essential for eye health and protection from age-related macular degeneration (Times of India).
❤️ 2. Heart Health
Daily pistachio consumption may help lower bad cholesterol (LDL) and raise good cholesterol (HDL), reducing the risk of heart disease. The nut’s healthy fats and plant sterols contribute to improved cardiovascular function (WebMD).
🍽️ 3. Supports Weight Management
Despite being energy-dense, pistachios are low in calories and high in protein, making you feel full longer. The act of shelling them also slows eating and helps with portion control (Healthline).
🌾 4. Good for Digestion
Pistachios are a great source of dietary fiber, which aids in gut health by promoting the growth of beneficial bacteria. Eating them daily can enhance bowel regularity (Medical News Today).
💪 5. High in Protein and Amino Acids
Pistachios are one of the highest-protein nuts, ideal for muscle repair and building. They also contain essential amino acids, including arginine, which improves blood flow (Healthline).
💡 6. Helps Control Blood Sugar
These nuts have a low glycemic index and are rich in healthy fats, protein, and fiber, which can help maintain steady blood sugar levels, especially beneficial for people with diabetes (Medical News Today).
✨ 7. Skin & Eye Health
The Vitamin E, carotenoids, and polyphenols in pistachios may reduce skin damage and enhance glow and protection from oxidative stress (Times of India).
🥜 Nutritional Snapshot (Per 28g serving)
| Nutrient | Amount |
|---|---|
| Calories | ~159 kcal |
| Protein | 6g |
| Fiber | 3g |
| Healthy fats | 13g |
| Vitamin B6 | 25% DV |
| Potassium | 6% DV |
| Phosphorus | 11% DV |
🛑 Things to Watch:
-
Choose unsalted and unroasted versions for maximum benefit.
-
Keep daily intake to about 28–56 grams (~1–2 ounces) to avoid excess calories.
✅ Summary: Why Eat Pistachios Daily?
| Benefit | Description |
|---|---|
| Antioxidants | Protects cells and eyes |
| Heart-friendly fats | Reduces bad cholesterol |
| Weight control | Promotes satiety |
| Gut health | Feeds good gut bacteria |
| Protein-rich | Supports muscles and metabolism |
| Blood sugar control | Lowers glycemic response |
| Skin & eye protection | Contains Vitamin E and carotenoids |
Related Products
- From Rs. 639.00
Rs. 650.00- From Rs. 639.00
- Unit price
- per
- From Rs. 639.00
Rs. 650.00- From Rs. 639.00
- Unit price
- per
- From Rs. 639.00
Rs. 650.00- From Rs. 639.00
- Unit price
- per
- From Rs. 639.00
Rs. 650.00- From Rs. 639.00
- Unit price
- per
Recently Viewed Products
- From Rs. 639.00
Rs. 650.00- From Rs. 639.00
- Unit price
- per
- From Rs. 639.00
Rs. 650.00- From Rs. 639.00
- Unit price
- per
- From Rs. 639.00
Rs. 650.00- From Rs. 639.00
- Unit price
- per
- From Rs. 639.00
Rs. 650.00- From Rs. 639.00
- Unit price
- per
